Milk Run Logistics: A Sustainable Solution for Reducing Carbon Emissions?
- April 25, 2024
- Blog
In supply chain logistics, an organisation is always on the lookout for new methods to optimise and streamline the logistics operations while transferring consignment from point A to point B. One popular strategy used by many of them is ‘Milk Run’. The term has been there for centuries, and today is an integral part of streamlining supply chain operations all across the world. Using this technique, one can optimise logistics through multi-pick, multi-drop, or even round-trip operations and meet sustainability goals.
The concept behind the word ‘Milk Run’
Milk Run was used by the dairy industry where one tank collected milk from various farms and delivered it to the milk processing firm. This same delivery method is nowadays used in logistics to optimise the delivery process using one vehicle which makes multiple stops helps improve efficiency in inventory management facilities and saves costs while making less emissions.
How does this concept work in supply chain logistics?
Milk Run, also known as cyclic goods taking, is a multi-pick, multi-drop, or round-trip system that enables seamless distribution. This business strategy involves consolidating transportation needs or combining all deliveries into a single trip utilising an efficient route map between all stops. This strategy reduces the need to use multiple vehicles simultaneously and reduces the impact of carbon emissions produced.
It is a method of goods collection & distribution where one truck follows a set route to visit various suppliers at scheduled intervals. In the case of an inventory management facility, items from multiple suppliers are first consolidated at the warehouse before being distributed to multiple stores or clients’ destinations.
The paper “Supply Chain System Model of Components for Assembly Lines Based on Kanban and Milk Run Methodologies,” published in the European Journal of Engineering and Technology Research, explains the concept of a milk run as “a collection method that defines an efficient route to reduce lead times for material delivery and collection.” The primary goal of milk-run logistics is to reduce travel time and costs in procuring raw materials or semi-finished products for production centres. However, this approach requires careful planning of routes and delivery schedules to avoid errors.
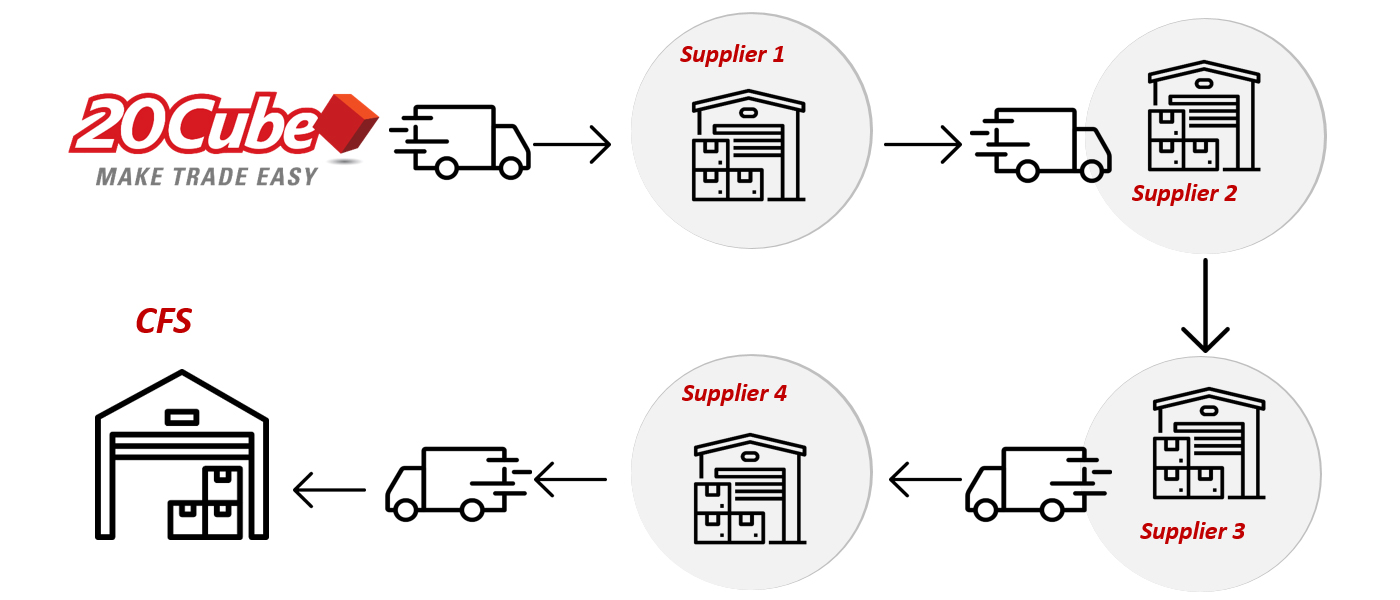
Let’s look at the benefits of the Milk Run model
Strengthen inventory management
The milk run model allows the supply chain logistics companies to manage their inventory efficiently and ensure that the stock is replenished, reducing the risk of stockouts. This results in less capital invested in inventory, improving cash flow and reducing the storage cost.
Reduction of waste
With better route planning and consolidation of shipments, there are fewer chances of waste being accumulated like packaging as it is designed around the specific needs of that particular milk run.
Better Quality Control
Handling smaller orders more frequently can make it easier to manage the details of each order, resulting in fewer quality problems. This is especially crucial when dealing with perishable goods or items at risk with low shelf-life.. Milk runs enable better control of these shipments, allowing faster responses if any quality issues arise.
Reduction in Carbon Emissions
Milk runs create an advantage to lower carbon emissions as one vehicle is operated instead of multiple vehicles to make a journey to multiple stops with meticulous route planning leading to lower carbon emissions helping companies to reach their sustainability goals.
How CO2 visibility assists shippers to manage & reduce milk run emissions
Supply chain companies like 20Cube Logistics are moving toward measuring and reducing their carbon footprint in distribution and utilising the resources effectively. But how is this done? This is done by tracking carbon emissions with full truckload rotation distances, vehicle and loading factors, and fuel consumption and then linking emissions to customer orders and can even track at the item level.
These detailed reports help understand their carbon footprint and reduce emissions, leading to real progress and marketable ESG initiatives.


